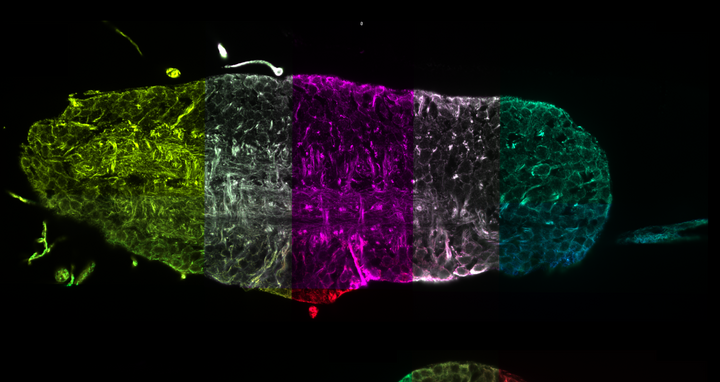
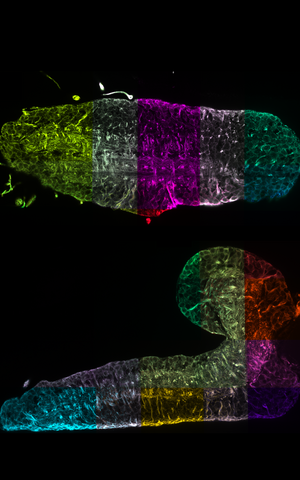
Google Maps for tissues
Two virtual right-angled cross-sections through the complete nervous system of a fruit fly larva. The combination of expansion microscopy, light sheet microscopy and data processing now makes it possible to reconstruct this complex organ optically with nanometer resolution. These data have the potential to track individual nerve cells without complex electron microscopy and thus significantly accelerate studies to investigate neuronal function. Each section highlighted in color is a large 3D image that has been automatically assembled like a mosaic into an overall image hundreds of gigabytes in size.
It works almost like a magic wand. With the help of a few chemical tricks and ruses, scientists have for a few years now been able to render large structures like mouse brains and human organoids transparent. CLARITY is perhaps the most well-known of the many different sample clearing techniques, with which almost any object of study can be made nearly as transparent as water. This enables researchers to investigate cellular structures in ways they could previously only dream o
And that’s not all. In 2015 another conjuring trick – called expansion microscopy – was presented in the journal Science. A research team at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge discovered that it was possible to expand ultrathin slices of mouse brains nearly five times their original volume, thereby allowing samples to be examined in even greater detail.
The software brings orders to the data chaos
“With the aid of modern light-sheet microscopes, which are now found in many labs, large samples processed by these methods can be rapidly imaged,” says Dr. Stephan Preibisch, head of the MDC research group on Microscopy, Image Analysis & Modeling of Developing Organisms. “The problem, however, is that the procedure generates such large quantities of data – several terabytes – that researchers often struggle to sift through and organize the data.”
To create order in the chaos, Preibisch and his team have now developed a software program that after complex reconstructing the data resembles somewhat Google Maps in 3D mode. “One can not only get an overview of the big picture, but can also zoom in to specifically examine individual structures at the desired resolution,” explains Preibisch, who has christened the software “BigStitcher.” Now, the computer program, which any interested scientist can use, has been presented in the scientific journal Nature Methods.
A team of twelve researchers from Berlin, Munich, the United Kingdom, and the United States were involved in the development. The paper’s two lead authors are David Hörl, from Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München and the Berlin Institute for Medical Systems Biology (BIMSB) of the MDC, as well as Dr. Fabio Rojas Rusak from the MDC research group of Professor Mathias Treier. The researchers show in their paper that algorithms can be used to reconstruct and scale the data acquired by light-sheet microscopy in such a way that renders a supercomputer unnecessary. “Our software runs on any standard computer,” says Preibisch. “This allows the data to be easily shared across research teams.“
3D view of a permanent-stage C. elegans larva. All cell nuclei are now clearly distinguishable for single cell examinations, the cell nuclei of the neurons are also stained red.
Data quality is also determined
The development of BigStitcher began about ten years ago. “At that time, I was still a PhD student and was thinking a lot about how to best handle very large amounts of data,” recalls Preibisch. “The frameworks we created back then have helped us to successfully tackle a very current problem.” But, of course, he adds, many new algorithms were also incorporated into the software.
BigStitcher can visualize on screen the previously imaged samples in any level of detail desired, but it can also do much more. “The software automatically assesses the quality of the acquired data,” says Preibisch. This is usually better in some parts of the object being studied than in others. “Sometimes, for example, clearing doesn’t work so well in particular area, meaning that fewer details are captured there,” explains the MDC researcher.
“The brighter a particular region of, say, a mouse brain or a human organ is displayed on screen, the higher the validity and reliability of the acquired data,” says Preibisch, describing this additional feature of his software. And because even the best clearing techniques never achieve 100 percent transparency of the sample, the software lets users rotate and turn the image captured by the microscope in any direction on screen. It is thus possible to view the sample from any angle. “This is another new feature of our software,” says Preibisch.
By combining complex data reconstruction and new developments in expansion microscopy, the team was able to visualize structures in a nanometer range for the complete nervous system of a fruit fly larva in 3D.
Anyone can download the software for free
The zoom function allows biologists to find answers to many questions, such as: Where in the brain is cell division currently taking place? Where is RNA expressed? Or where do particular neuronal projections end? “In order to find all this out, it is first necessary to get an overview of the entire object of study, but then to be able to zoom in to view the smallest of details in high resolution,” Treier and Preibisch agree. Therefore, many labs today have a need for software like BigStitcher. The program is distributed within the Fiji framework, where any interested scientist can download and use the plug-in free of charge.
Anke Brodmerkel
Like Google Maps in 3D for the mouse brain: With the "BigStitcher" software you can reconstruct a sample and then rotate and turn it virtually, get an overview of the big picture or zoom into individual structures. This works both as a user, as illustrated here, and as an algorithm that analyzes the data and cannot load the entire image into RAM. Neurons expressing a specific gene are marked in green. Such data now make it possible for the first time to systematically characterize differences at the single-cell level between normal and genetically modified mice and to draw conclusions about potential behavioral changes that may result.
Further information
Literature
David Hörl, Fabio Rojas Rusak et al. (2019): „BigStitcher: Reconstructing high-resolution image datasets of cleared and expanded samples“. Nature Methods, doi 10.1038/s41592-019-0501-0.
Contacts
Dr. Stephan Preibisch
Head of the Lab “Microscopy, Image Analysis & Modeling of Developing Organisms” at the Berlin Institute of Medical Systems Biology (BIMSB)
Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC)
+49(0)30-9406-1353
Stephan.Preibisch@mdc-berlin.de
Jana Schlütter
Editor, Communications Department
Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC)
+49(0)30-9406-2121
jana.schluetter@mdc-berlin.de
- The Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC)
-
The Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC) is one of the world’s leading biomedical research institutions. Max Delbrück, a Berlin native, was a Nobel laureate and one of the founders of molecular biology. At the MDC’s locations in Berlin-Buch and Mitte, researchers from some 60 countries analyze the human system – investigating the biological foundations of life from its most elementary building blocks to systems-wide mechanisms. By understanding what regulates or disrupts the dynamic equilibrium in a cell, an organ, or the entire body, we can prevent diseases, diagnose them earlier, and stop their progression with tailored therapies. Patients should benefit as soon as possible from basic research discoveries. The MDC therefore supports spin-off creation and participates in collaborative networks. It works in close partnership with Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin in the jointly run Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC), the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH) at Charité, and the German Center for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK). Founded in 1992, the MDC today employs 1,600 people and is funded 90 percent by the German federal government and 10 percent by the State of Berlin.