New treatment approach for rare blood cancer of the skin
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a rare form of blood cancer that primarily affects the skin. In Europe, the disease is diagnosed in about 0.5 per 100,000 inhabitants per year. Advanced stages are associated with a poor prognosis and quality of life.
A team of researchers led by Professor Olaf Merkel in the Department of Experimental Pathology at Medical University of Vienna and Professor Stephan Mathas at the Experimental and Clinical Research Center, a joint institution of the Max Delbrück Center and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, points to CD74 protein as a promising new target for innovative therapies to treat CTCL. In a preclinical model, the researchers showed that so-called antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), which specifically bind to CD74, can effectively kill CTCL cells.
New therapeutic approach for a difficult-to-treat disease
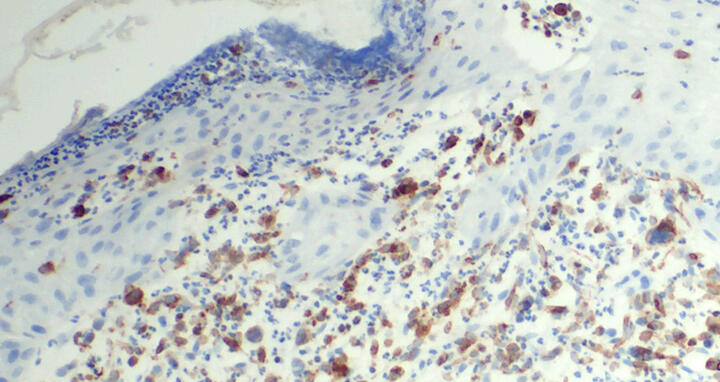
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma with transformed cells (CD74 labeled in brown; skin cells are in blue).
Although monoclonal antibodies and ADCs are already successfully being used to induce remission in CTCL patients, existing treatments do not provide a cure. ADCs that target CD74 offer a potentially new treatment approach. The research team showed that CD74 is strongly and consistently expressed in various CTCL subtypes, including particularly difficult-to-treat forms such as Sézary syndrome and advanced stages of mycosis fungoides.
“Our results show that CD74 is not only an attractive target molecule for antibody therapy, but that its blockade can lead to complete tumor eradication in preclinical models,” says Merkel. It is particularly noteworthy that the treatment was highly effective even in TP53-defective CTCL cells - an aspect of great clinical relevance. TP53 is an important tumor suppressor gene that is mutated in many cancers.
The basis for future clinical studies
The study findings provide a solid basis for further developing new antibody-based treatments that target CD74 and pave the way for clinical trials. “Our results open up new perspectives for the treatment of CTCL patients who currently have inadequate treatment options,” add the study authors.
The researchers see CD74-targeted therapy as an especially promising approach to improve treatment for patients with advanced CTCL, who currently have very limited options.
Further Information
Literature
Mariantonia Costanza, Catello Giordano, Ann-Christin von Brünneck, et. al. (2025) “Preclinical in vitro and in vivo evidence for targeting CD74 as an effective treatment strategy for cutaneous T-cell lymphomas.” British Journal of Dermatology. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/bjd/ljaf001